RS and AS in Tucnak: Difference between revisions
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
* '''OpenSkyNetwork''' - free but not very available service. Keep username and pasword blank for unregistered access. Keep the Interval high, [https://openskynetwork.github.io/opensky-api/rest.html#api-credit-usage not to drain your credits]. Beware if you have more computers! | * '''OpenSkyNetwork''' - free but not very available service. Keep username and pasword blank for unregistered access. Keep the Interval high, [https://openskynetwork.github.io/opensky-api/rest.html#api-credit-usage not to drain your credits]. Beware if you have more computers! | ||
=The Map= | |||
[[Image:RSAS_AircraftMap.png|thumb|none|960px|Aircraft map]] | [[Image:RSAS_AircraftMap.png|thumb|none|960px|Aircraft map]] | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 15 November 2023
Have you ever heard about the Rain Scatter (RS) propagation, or the Aircraft Scatter (AS)? Would you like to try it? If you'd like, let's take a look how it can be managed thanks to Tucnak.
Especially in the case of AS it's always better to schedule a sked instead of trying a random QSO. To do so ON4KST chat is the best option. Tucnak allows the combined use of this chat and AS / RS functions to make these operations easier.
ON4KST
Setup ON4KST credentials in the Setup/Contest defaults. You should fill in KST Username (which is in fact your callsign) and your password. It is also recommended to fill in KST Yourname by your first name. People usually add bands that they are active on, eg 3cm.
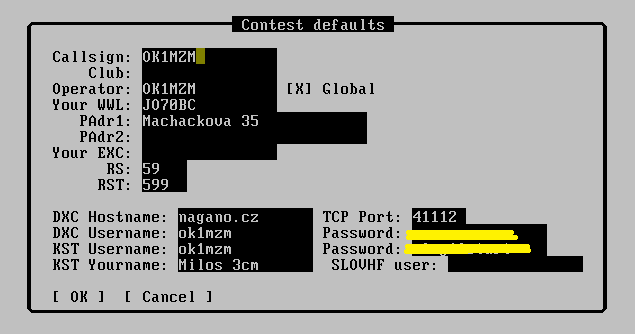
Once KST configuration is set up, press enter in the KST window and select a chat room. Since you are interested in RS/AS your option is most likely “3” (Microwave).
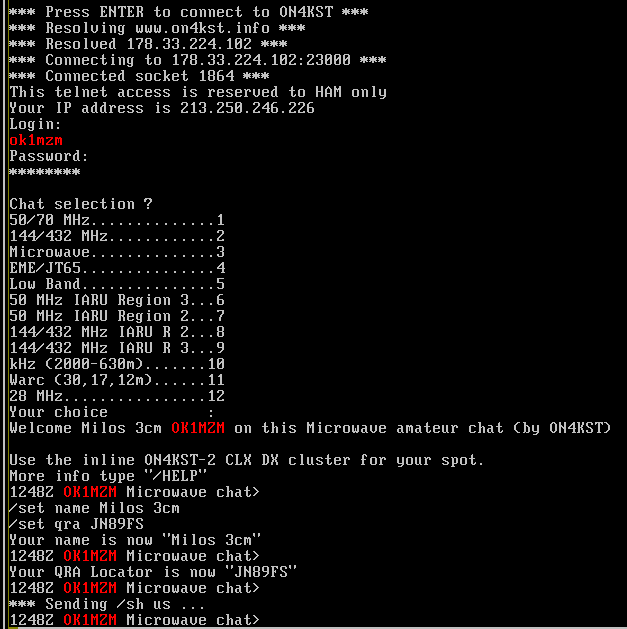
Once you are logged in the chat six columns in right start to fill up.
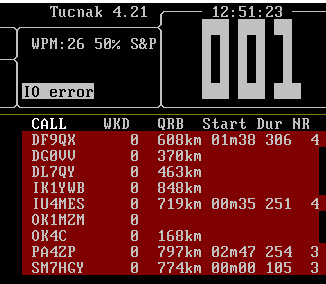
The first column CALL is filled with callsigns of people logged in the chat. You may want to try left click on a specific call. It will select the call. Repeated left click deactivate the selection. Once selected most of the calls will appear yellow, but sometimes they can be green. Yellow color marks stations you don't have in your log. Once a QSO is completed and logged, such a station changes its color to brown-green. Thanks to this color recognition you can easily distinguish what stations you have not made a QSO with.
There is also an option to hide all stations which are located at a greater distance than the set limit in Setup/Contest defaults/A/C options/Maximal QRB for KST
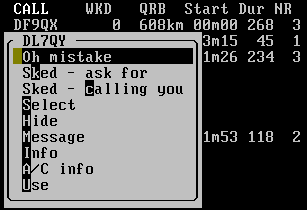
There is also a right click menu available. Let's describe the most important options in this menu:
- Sked - ask for (can be activated by pressing “k” key once the right click menu is active)
- creates a message with predefined text asking for a sked on active band
- Sked - calling you
- creates similar message as the first option, but this one is longer
- Hide
- hide the station from the list on the right. Repeated click unhide the station
- Message
- creates an empty message (this is a frequently used option)
- Use
- fill in the call into the input line (this is a frequently used option)
You may have noticed some words in the KST window are red. Tucnak highlights such words like later, tnx, 73 etc. to alert you to a station which ends a correspondence with another station. It's supposed that such a station just has time for a sked. The probability that such a station answers your request is very high.

There is also another function that points out to you a station that just might have time for a sked because it just logged in to KST and is not in a sked with another station. Such stations are marked by a red line/background.

The Map window
Move the mouse cursor over the map to see details of the specific place on the right. The most useful information is QRB (distance), QTF (azimuth) and Loc (WWL locator). Both first parameters are calculated from your own position (Your WWL in the Contest options).
Rain Scatter
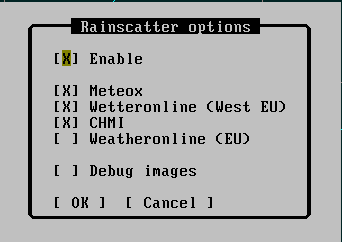
First of all, you should turn on the RS option in Tucnak.(Setup/Rainscatter options). If everything goes well you should see clouds in the Map window.
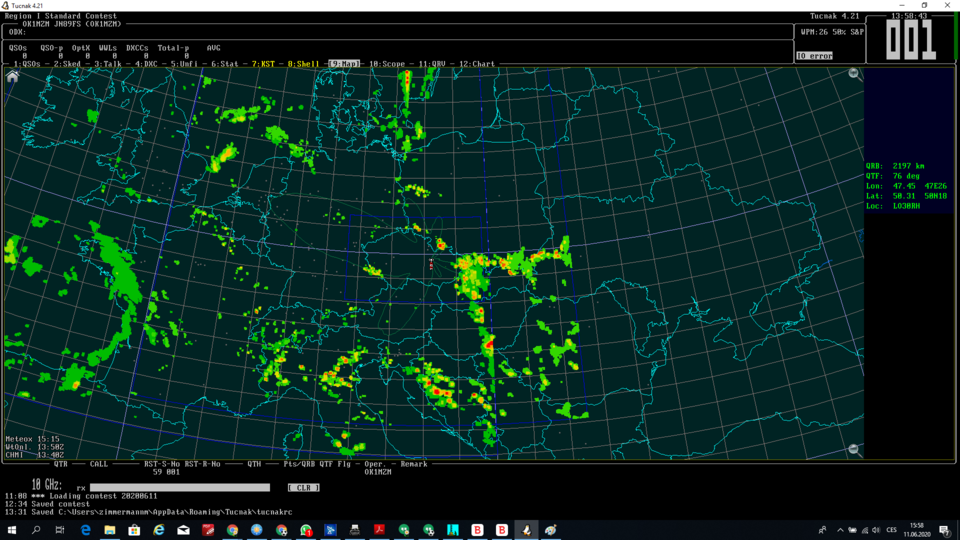
Move the mouse cursor over the clouds in the Map window to find a suitable SCP (scatter point). The information indicated on the right shows QRB, QTF and WWL locator of the SCP chosen. Both stations turn their antennas to the SCP. An SCP can be in line between both stations,or behind one of the stations (backscatter). Backscattering is a bigger challenge due to the bigger distance of the SCP from one of the stations.
Aircraft Scatter
First of all, you should turn on the AS options in Tucnak.(Setup/Setup/A/C options). If everything goes well you should see aircrafts in the Map window.
NEW: Please read Aircraft scatter 2023
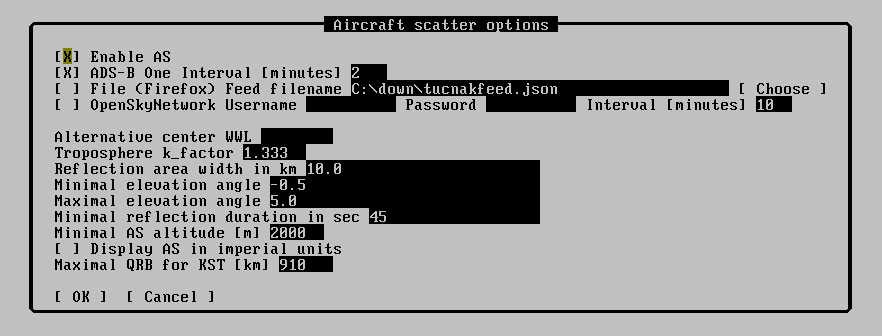
- Enable AS - enable or disable all Aircraft Scatter features
- File (Firefox) - use aircraft data from local file.
- OpenSkyNetwork - free but not very available service. Keep username and pasword blank for unregistered access. Keep the Interval high, not to drain your credits. Beware if you have more computers!
The Map
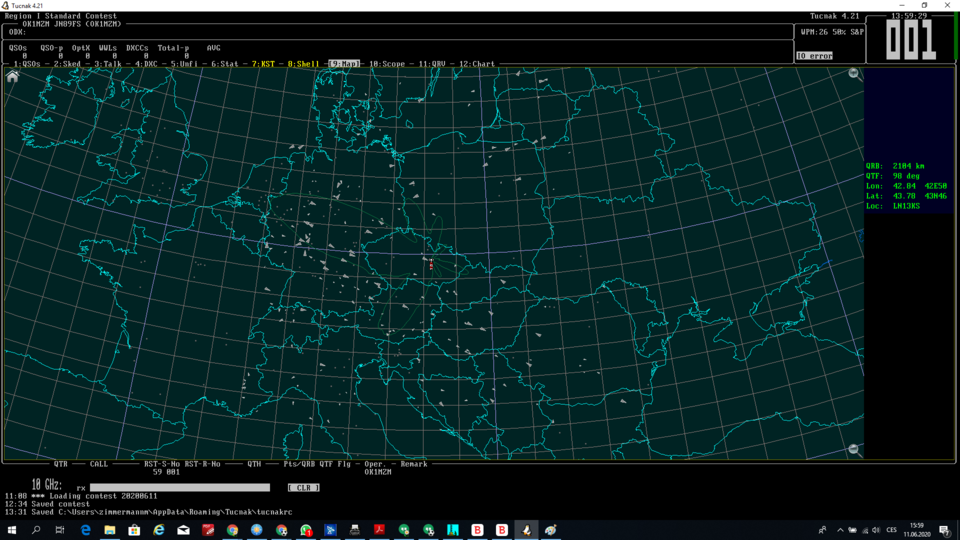
Let's assume you are in the KST window and logged into the ON4KST chat room.
The list on the right serves to show you which the stations logged in KST are suitable for AS operation.
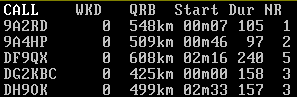
The most important is Start and Dur (duration; in minutes). These two parameters specify when the reflection should start and how long it will take. You can sort the columns by left clicking on a column´s name. NR stands for a number of aircrafts that form the predicted reflection. Right clicking on a station with which you would like to make a QSO will open a menu. The option A/C info opens a map preview between you and selected station (WWL comes from the QRV database).
A yellow shows a reflective zone. An aircraft should be in this yellow zone to make an AS QSO. Aircrafts that are considered by Tucnak as usable will be marked by blue color. The gray ones were evaluated as non usable (out of reflection area, low altitude). However, aircrafts are moving thus it can be reevaluated anytime. Blue aircrafts have a line in the direction of their flight. It helps you to imagine where they will cross the yellow zone.
Aircrafts are represented by triangles and their sizes are derived from real sizes of the aircrafts. As larger aircrafts usually give stronger reflections you may want to look for such aircrafts. Also have in mind that different flight paths give different reflections. If an aircraft flies along the line between you and the station the reflection will be longer and the Doppler effect will be theoretically zero. On the contrary, perpendicular flight will be short and the Doppler effect will be strong, especially on higher bands. The exact position of aircrafts are centers of triangles. Aircrafts positions match their real positions - there is almost zero delay.
Once you place the cursor on an aircraft (no click is needed) information about the aircraft will appear in the right upper corner of the preview.
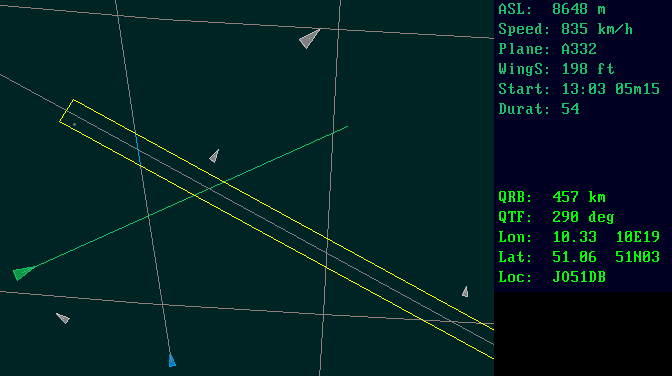
Such information enables you to better understand the situation. The most important is Start and Durat as explained above.
So far we have described how to use Tucnak for the AS operation using the KST chat room. However, it is possible to use Tucnak´s AS functions without KST as well. You should open the Map window and type a call into the input line. Use of the Map window is similar to the Map preview in the KST window described above.
73 Miloš, OK1MZM